The autonomic nervous system (ANS) [स्वतंत्र तंत्रिका प्रणाली], formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates internal organs, smooth muscle, and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response. Although conflicting reports about its subdivisions exist in the literature, the autonomic nervous system has historically been considered a purely motor system and has been divided into three branches: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), and the enteric nervous system (ENS).
Definition of Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a division of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. It operates largely below the level of consciousness and regulates internal organs to maintain homeostasis, responding to various stimuli to keep the body functioning properly. The ANS consists of two main branches: the sympathetic nervous system, which prepares the body for “fight or flight” responses, and the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes relaxation and “rest and digest” activities. These two branches often work in opposition to maintaining balance in the body’s functions.
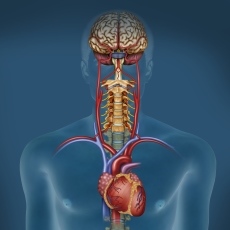
Meaning of Autonomic Nervous System
The term “autonomic nervous system” refers to a complex network of nerves and ganglia that regulate involuntary bodily functions. “Autonomic” denotes the system’s ability to function independently, without conscious control, to regulate various physiological processes essential for survival and homeostasis. The autonomic nervous system controls vital functions such as heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and temperature regulation. It ensures that these processes operate automatically and adaptively, responding to internal and external stimuli to maintain optimal conditions within the body.
How many are the divisions of Autonomic Nervous Systems?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) consists of three divisions i.e. Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS), the Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS), and the Enteric Nervous System (ENS):
- Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): This division is often associated with the body’s “fight or flight” response. It prepares the body for action in response to stress or danger by increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and redirecting blood flow to muscles.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS): This division is often referred to as the “rest and digest” system. It promotes relaxation and conservation of energy by slowing heart rate, constricting pupils, and stimulating digestion.
- The Enteric Nervous System (ENS) is often referred to as the “second brain” due to its complexity and ability to function semi-autonomously from the central nervous system (CNS). It is the third division of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), alongside the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
These three divisions of the autonomic nervous system often work in opposition to each other to maintain balance (homeostasis) in the body’s functions.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a crucial part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. It operates automatically and unconsciously to maintain homeostasis within the body, responding to various internal and external stimuli.
How does the Autonomic Nervous System benefit the human body?
How Autonomic Nervous System Functions?
What are the caffeine effects on the Autonomic Nervous System?
What are the dysfunctions of the Autonomic Nervous System?
Conclusion
In conclusion, the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a vital component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary bodily functions crucial for survival and adaptation to the environment. Through its two main divisions, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, the ANS maintains homeostasis by modulating processes such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and respiratory rate. While the ANS plays a critical role in optimizing physiological responses and supporting overall health, dysfunctions or disorders affecting its regulation can lead to a wide range of symptoms and health problems. Understanding the role of the ANS in maintaining bodily functions is essential for diagnosing and treating autonomic disorders and promoting well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autonomic_nervous_system

xs0mdg
Thanks for your prompt and soothing response. I’m highly obliged of your kind attitude. Please stay tuned and have a nice day!!
вывод из запоя дешево ростов https://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov15.ru .